FLAT 10% OFF ON YOUR FIRST ORDER. USE IVER10
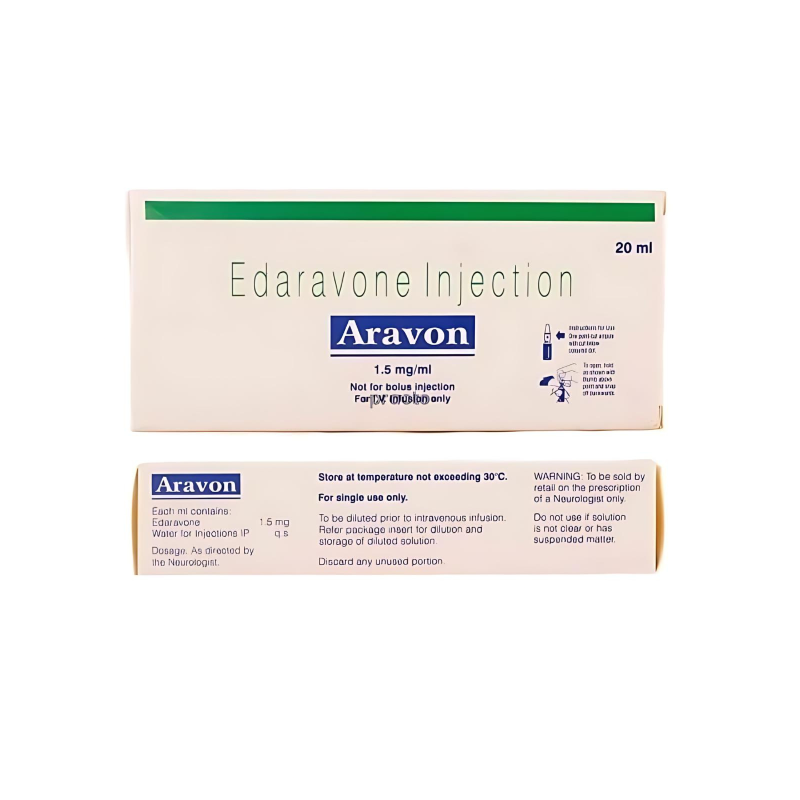
Aravon Injection (Edaravone)
Price range: $88.00 through $239.00
Aravon Injection, powered by Edaravone, is a neuroprotective therapy used in the treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and for limiting neurological damage in ischemic stroke. It works by eliminating harmful free radicals and reducing oxidative stress in the nervous system, helping slow the progression of nerve damage and supporting recovery outcomes in stroke patients. Administered via IV infusion by healthcare professionals, Aravon is especially effective when given within 24–72 hours after a stroke. Though not a cure for ALS, it improves quality of life and muscle function over time.
- Buy 2 and get Flat 15% Off. Use B2SAVE15
- Buy 3 and get Flat 20% Off. Use B3SAVE20
Aravon Injection (Edaravone) – Treatment for ALS & Ischemic Stroke Neuroprotection
Aravon Injection is a neuroprotective medication used to treat amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and reduce neurological damage caused by ischemic stroke. It works by combating oxidative stress, slowing nerve degeneration, and protecting brain cells. Administered intravenously by healthcare professionals, it is prescribed when oral medications aren’t viable. Common side effects include headache, gait disturbances, and mild injection-site reactions. Though generally safe for liver/kidney patients, pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult a doctor before use. Early administration (within 24-72 hours post-stroke) maximizes its neuroprotective benefits. While it cannot cure ALS, it significantly slows disease progression and improves quality of life.
Uses of Aravon Injection:
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
- Neuroprotection in ischemic stroke
- Traumatic brain injury
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Parkinson’s disease dementia
- Age-related cognitive decline
Benefits of Aravon Injection:
In ALS
Aravon Injection delays nerve damage progression in ALS, helping maintain muscle strength for daily activities like walking, speaking, and swallowing. This preserves independence longer.
In Ischemic Stroke
By neutralizing harmful free radicals, it minimizes brain cell death during stroke, improving recovery outcomes when administered early.
Side Effects of Aravon Injection:
Common (usually mild):
- Headache
- Gait disturbance (walking difficulty)
- Injection-site pain/redness
Serious (rare): Allergic reactions (swelling, itching). Seek immediate medical help if these occur.
How to Use Aravon Injection?
Administered only by healthcare professionals via intravenous infusion. Typical regimen:
- Initial cycle: Daily for 14 days, followed by 14-day rest period.
- Subsequent cycles: Daily for 10 days per 28-day cycle.
How Aravon Injection Works?
As a potent antioxidant, it scavenges free radicals that cause oxidative stress in nerve cells. This neuroprotective action:
- Slows ALS progression by protecting motor neurons.
- Reduces brain damage during ischemic stroke by preventing lipid peroxidation.
Safety Advice:
- Alcohol: Consult doctor—interaction data unavailable.
- Pregnancy/Breastfeeding: Avoid unless absolutely necessary.
- Driving: Caution advised—may cause dizziness.
- Kidney/Liver Disease: Safe at prescribed doses.
What If You Miss a Dose?
Contact your healthcare provider immediately to reschedule. Never double the dose.
FAQs:
Q1. Can Aravon Injection cure ALS?
No, but it slows disease progression by approximately 33%, helping preserve muscle function longer.
Q2. When should it be given after a stroke?
Ideally within 24-72 hours for maximum neuroprotection.
Q3. Why is it used more in veterans/athletes?
Higher ALS risk in these groups may be linked to toxin exposure (military service) or physical stress (athletes).
Q4. Are there genetic risks for ALS?
5-10% of cases are familial (inherited). Most are sporadic with unknown causes.
Q5. How is the injection administered?
IV infusion over 60 minutes in clinical settings, following specific cyclic protocols.
Q6. Can it reverse stroke damage?
No, but it limits further damage by protecting vulnerable brain cells.
| Strength | 1.5 mg |
|---|---|
| Pack Size | 1 Injection, 2 Injection, 3 Injection |






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.