FLAT 10% OFF ON YOUR FIRST ORDER. USE IVER10
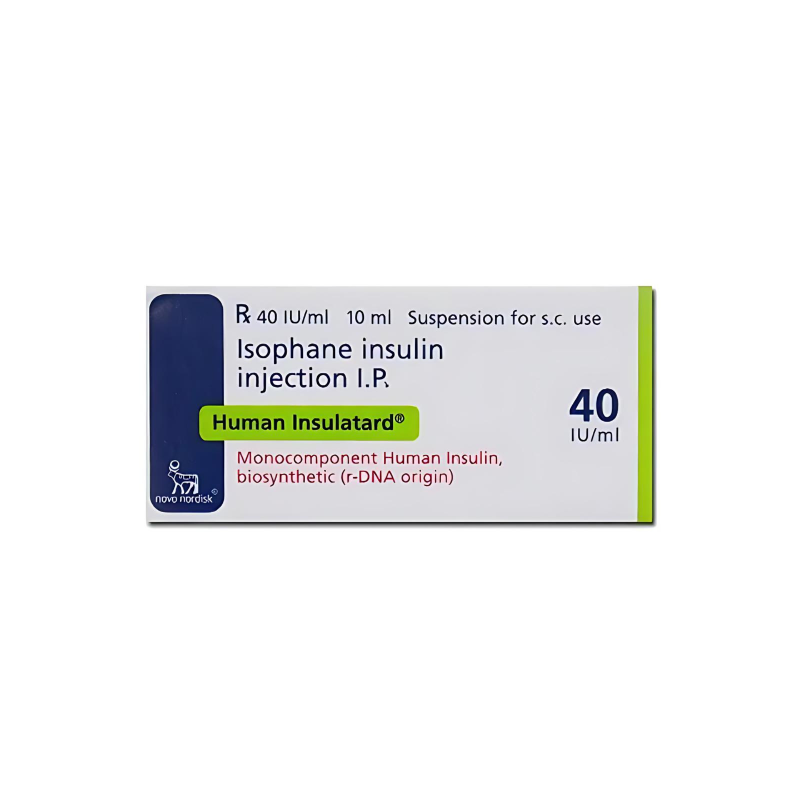
Human Insulatard Suspension for Injection (Insulin Isophane)
Price range: $33.00 through $155.00
Human Insulatard Suspension for Injection is a premixed insulin formulation combining short-acting regular insulin with intermediate-acting isophane insulin (NPH). Designed for effective blood glucose control in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, this dual-action therapy provides both rapid and sustained insulin coverage throughout the day. Administered subcutaneously, it mimics the body’s natural insulin response when used alongside a proper diet, exercise, and regular monitoring. Typically dosed twice daily, it helps manage both mealtime spikes and basal glucose levels. Patients should consume a carbohydrate-rich meal within 30 minutes of injection to avoid hypoglycemia. Side effects may include injection site irritation, mild weight gain, or low blood sugar. Store unopened vials in the refrigerator and use opened ones within 6 weeks at room temperature. Safe for pregnant and breastfeeding women under medical supervision. Always consult a doctor before starting or adjusting insulin therapy.
- Buy 2 and get Flat 15% Off. Use B2SAVE15
- Buy 3 and get Flat 20% Off. Use B3SAVE20
Human Insulatard Suspension for Injection (Biphasic Isophane Insulin) – Dual-Action Diabetes Treatment
Human Insulatard Suspension for Injection is a premixed insulin formulation combining intermediate-acting insulin isophane (NPH) with short-acting regular human insulin. This dual-action therapy provides both rapid onset and prolonged duration of blood sugar control, making it ideal for managing Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in adults and children. Administered subcutaneously, it effectively mimics the body’s natural insulin response when used as part of a comprehensive treatment plan including diet control, exercise, and regular glucose monitoring. Patients must consume a carbohydrate-rich meal within 30 minutes post-injection to optimize glycemic control and prevent hypoglycemia.
Uses of Human Insulatard Suspension for Injection:
- Management of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (insulin-dependent)
- Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes when oral medications fail
- 24-hour blood glucose control with twice-daily dosing
Benefits of Human Insulatard Suspension for Injection:
This biphasic insulin offers convenient blood sugar management by combining rapid meal-time coverage with sustained basal control. The premixed ratio (typically 70% isophane/30% regular) reduces injection frequency while maintaining stable glucose levels. Clinical studies demonstrate reduced risks of long-term diabetic complications including retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy when optimal glycemic control is achieved.
Side Effects of Human Insulatard Suspension for Injection:
- Very common: Hypoglycemia (sweating, tremors, confusion)
- Common: Injection site reactions (pain, erythema, lipodystrophy)
- Occasional: Weight gain, allergic skin reactions, peripheral edema
How to Use Human Insulatard Suspension for Injection?
- Gently roll the vial to resuspend before drawing dose
- Inject subcutaneously in abdomen, thighs, or upper arms
- Rotate injection sites to prevent lipohypertrophy
- Administer 30 minutes before meals containing carbohydrates
- Unopened vials: Refrigerate at 2-8°C
- In-use vials: Store at room temperature (≤25°C) for ≤6 weeks
How Human Insulatard Suspension for Injection Works?
The regular insulin component provides rapid onset (30-60 minutes) to control postprandial spikes, while isophane insulin delivers intermediate action (peak 4-12 hours) for sustained basal coverage. Together they facilitate cellular glucose uptake in peripheral tissues while suppressing hepatic gluconeogenesis, mimicking physiological insulin secretion patterns.
Safety Advice:
- Alcohol: Absolutely avoid – potentiates hypoglycemia
- Pregnancy: Safe with medical supervision (dose adjustments likely)
- Breastfeeding: Compatible – minimal transfer to breastmilk
- Driving: Test blood sugar before operating vehicles/machinery
- Renal/Hepatic Impairment: Requires dose reduction & frequent monitoring
What If You Missed a Dose?
Check blood glucose immediately. For hyperglycemia (>200 mg/dL), administer 50% of missed dose and monitor closely. Never double dose to compensate. Maintain consistent meal timing to prevent glycemic fluctuations.
FAQs:
Q1: How should I mix Human Insulatard properly?
Gently roll the vial 10 times (don’t shake) until the suspension appears uniformly cloudy. Inspect for clumping or discoloration before use.
Q2: Can I switch from other insulin to Human Insulatard?
Transition requires medical supervision. Dose ratios differ significantly between insulin types – consult your doctor for proper conversion protocols.
Q3: Why must I eat within 30 minutes after injection?
The regular insulin component begins working within 30 minutes. Delaying meals risks dangerous hypoglycemia as glucose absorption can’t match insulin activity.
Q4: How do I recognize severe hypoglycemia?
Symptoms progress from sweating/confusion to seizures/loss of consciousness. Treat immediately with oral glucose (15-20g) or glucagon injection if unconscious.
Q5: What’s the best injection site rotation pattern?
Systematically rotate between abdominal quadrants, thighs, and upper arms. Track sites to avoid repeating within 1-inch radius for ≥1 month.
Q6: Can I use expired Human Insulatard?
Never use expired insulin. Altered potency may cause uncontrolled hyperglycemia or unexpected hypoglycemia from degraded components.
Q7: How often should I check my blood sugar?
Minimum 4x daily (fasting + postprandial). More frequent monitoring needed when adjusting doses, during illness, or if hypoglycemia occurs.
| Pack Size | 1 Injection, 2 Injection, 3 Injection |
|---|






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.