FLAT 10% OFF ON YOUR FIRST ORDER. USE IVER10
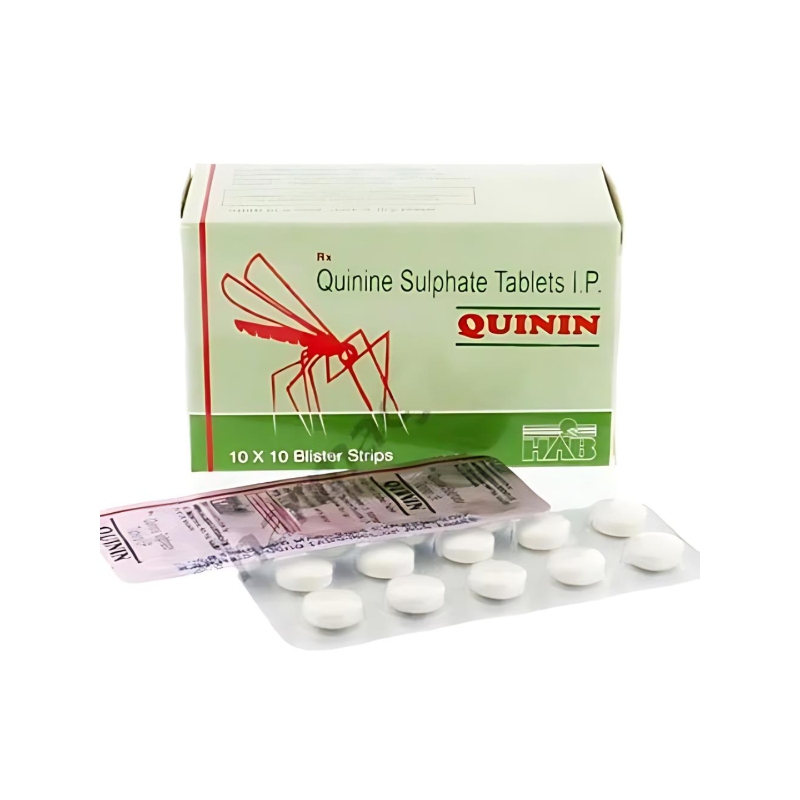
Quinin Tablet (Quinine Sulphate)
Price range: $112.00 through $212.00
Quinin Tablet is a time-tested antimalarial medication used for the treatment of uncomplicated malaria, especially in areas with chloroquine-resistant Plasmodium falciparum. Derived from the cinchona bark, it targets blood-stage parasites, providing rapid symptom relief. It is typically taken every 8 hours with food for 3–7 days, depending on the infection’s severity and your doctor’s guidance. Quinin is often used in combination therapies to improve efficacy and reduce resistance. Common side effects include nausea, tinnitus (ringing in ears), and mild dizziness, which usually subside with continued use. Always complete the full course to prevent relapse. Now available online at Ivermectins.com, your trusted global pharmacy. We offer fast, secure shipping to the US, UK, Australia, and many more countries. Order now and enjoy free delivery options and reliable service for your antimalarial needs.
- Buy 2 and get Flat 15% Off. Use B2SAVE15
- Buy 3 and get Flat 20% Off. Use B3SAVE20
Quinin Tablet – Treatment for Malaria
Quinin Tablet is an established antimalarial medication used to treat active malaria infections caused by Plasmodium parasites. Derived from the bark of the cinchona tree, this formulation specifically targets malaria parasites in the red blood cells. While highly effective for treatment, it does not prevent malaria infection. The tablet is typically prescribed for 3-7 days, taken every 8 hours with food to minimize gastrointestinal discomfort. Dosage varies based on infection severity, patient age, and regional treatment protocols, with pediatric doses calculated by weight. As malaria strains and resistance patterns differ geographically, always follow your healthcare provider’s specific instructions for optimal results.
Uses of Quinin Tablet:
- Treatment of uncomplicated malaria infections
- Management of chloroquine-resistant Plasmodium falciparum malaria
- Adjunctive therapy for severe malaria cases
Benefits of Quinin Tablet:
Quinin Tablet provides:
- Proven efficacy against malaria parasites in red blood cells
- Treatment option for resistant malaria strains
- Rapid action to control malaria symptoms
- Flexible dosing based on patient needs
Side Effects of Quinin Tablet:
Common side effects may include:
- Nausea and stomach discomfort
- Ringing in ears (tinnitus)
- Headache and dizziness
- Visual disturbances
- Mild hearing impairment
These symptoms often resolve as treatment continues. Contact your doctor if persistent.
How to Use Quinin Tablet?
Take exactly as prescribed:
- Swallow whole with water
- Take with food to reduce stomach upset
- Maintain strict 8-hour dosing schedule
- Complete full course even if symptoms improve
- For children, dose is weight-dependent
How Quinin Tablet Works?
Quinine combats malaria through multiple mechanisms:
- Interferes with parasite’s ability to digest hemoglobin
- Accumulates toxic heme molecules within parasites
- Disrupts parasite metabolism and DNA replication
- Ultimately kills blood-stage malaria parasites
Safety Advice:
- Alcohol: Avoid – may increase side effects
- Pregnancy: Use only if clearly needed
- Breastfeeding: Consult doctor – small amounts pass to milk
- Driving: Caution advised – may cause dizziness
- Heart Conditions: Requires ECG monitoring
- G6PD Deficiency: Increased risk of complications
What If You Missed a Dose?
Take the missed dose as soon as remembered. If near next dose time, skip the missed dose. Never double dose to compensate.
FAQs:
Q1. Why must Quinine be taken with food?
Food improves absorption and reduces gastrointestinal irritation, a common side effect.
Q2. Can Quinine cure malaria in one dose?
No, complete treatment requires the full prescribed course (typically 3-7 days) to ensure all parasites are eliminated.
Q3. Why does Quinine cause ringing in ears?
This “cinchonism” effect occurs due to quinine’s impact on nerve cells and usually resolves after treatment ends.
Q4. Can I take Quinine for leg cramps?
No, this use is no longer recommended due to potential serious side effects.
Q5. How should I store Quinine tablets?
Keep in original packaging at room temperature (15-30°C), away from moisture and light.
Q6. What should I do if I experience vision changes?
Stop taking immediately and contact your doctor, as this may indicate quinine toxicity.
| Strength | 300 mg |
|---|---|
| Pack Size | 60 Tablets, 90 Tablets, 120 Tablets |





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.